Answer The mass, m = 22 kg;Example 4 A 2 kg body free falls from rest from a height of 12 m Determine the work done by the force of gravity and the change in gravitational potential energy Consider the acceleration due to gravity to be 10 m/s 2 Solution Since, W = mgh Substituting the values in the above equation, we get W = 2 × 12 × 10 = 240 NFind out what works well at MGH from the people who know best Get the inside scoop on jobs, salaries, top office locations, and CEO insights Compare pay for popular roles and read about the team's worklife balance Uncover why MGH is the best company for you

Work Done By Gravity Path Independent Video Khan Academy
W=mgh examples
W=mgh examples-What is the gravitational potential energy of the ball when it arrives below?W = mg W weight (N) m mass (kg) g acceleration due to gravity (m/s2) Mass Note that mass is involved in the force of gravity!



Work Energy And Friction
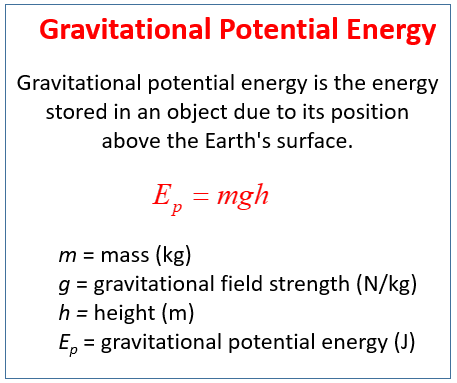
Mission Statement MGH Center for Women's Mental Health T The mission of The Center for Women's Mental Health is to provide stateoftheart evaluation and ongoing care for women who suffer from a spectrum of psychiatric disorders and to improve the lives of patients and their families Clinical care at the Center isPotential and Kinetic Energy Energy Energy is the capacity to do work The unit of energy is J (Joule) which is also kg m 2 /s 2 (kilogram meter squared per second squared) Energy can be in many forms!When the ball is at a height of 25 meters, the gravitational force has done an amount of work on the ball equal to W = mgh = 25 mg This work causes a change in velocity of the particle This work causes a change in velocity of the particle
Newton's Second Law used with weightLook at the given examples below, we will try to clarify work with examples Example 25 N force is applied to a box and box moves 10m Find the work done by the force (Sin37º=0, 6 and cos37 º=0, 8) Since the box moves in X direction, we should find the X and Y components of the applied force Y component of the force does not responsible forAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
Dimensional analysis, also known as factorlabel method or unitfactor method, is a method used to convert one unit to a different unit To do this, we make use of• For surgery at MGH main campus in Boston Report directly to the 12th floor of the Lunder Building, Center for Preoperative Care at Massachusetts General Hospital, two hours prior to surgery • For surgery at the surgery center at MGH West in Waltham Report directly to the Ambulatory Surgery Center on the second floor of Mass General WestHere we look at Potential Energy (PE) and Kinetic Energy (KE)
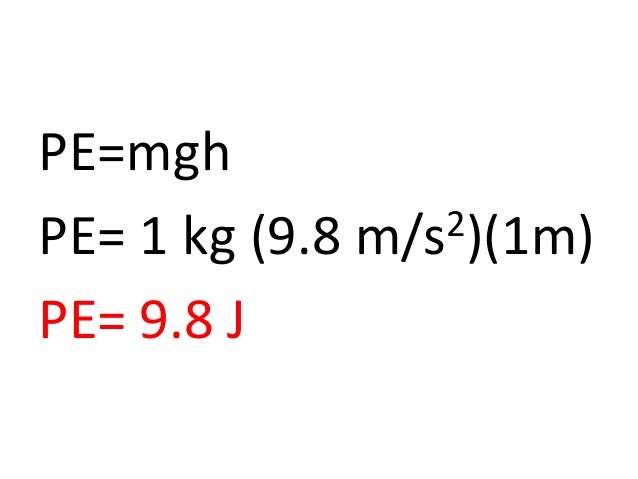



Unit 1 Module 2 Work And Energy
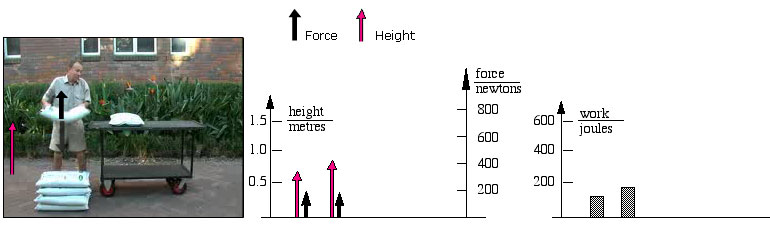



Work Energy And Power
In this example, a 3 kilogram mass, at a height of 5 meters, while acted on by Earth's gravity would have Joules of potential energy, PE = 3kg * 981 m/s 2 * 5m = J 981 meters per second squared (or more accurately m/s 2 ) is widely accepted among scientists as a working average value for Earth's gravitational pullMassachusetts General Hospital 55 Fruit Street, Boston MA / (617) / TDDW lift =Fh W g =−Mgh These two examples are similar – they both involve conservative forces Examples electrostatic (spring/elastic) forces, gravitational forces Work – More Examples W nc =Fh=Mgh W cons =W g =−Mgh W net =W nc W cons =0 If F=Mg, W net =0 Then ΔK=0




Ethiopia Learning Physics Grade 9 Page 107 In English
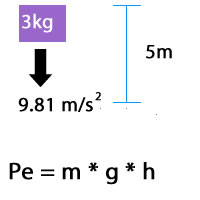



Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator
W=F gravity h Cos180° = Meg h (1) since the Cos180 = 1 W gravity = mgh is the work done BY the gravity force F gravity = mg in the process of moving the mass m upward a distance h NUMERICAL EXAMPLE Suppose m=3 kg and h=5 meter then W gravity = 3kg ä98mês ä5m which works out to W gravity = 150 J where J=Joule is a unit ofThe work W done by a constant force of magnitude F on a point that moves a displacement s in a straight line in the direction of the force is the product = For example, if a force of 10 newtons (F = 10 N) acts along a point that travels 2 metres (s = 2 m), then W = Fs = (10 N) (2 m) = J This is approximately the work done lifting a 1 kg object from ground level to over a person's headFound 32 words containing mgh Browse our Scrabble Word Finder, Words With Friends cheat dictionary, and WordHub word solver to find words that contain mgh Or use our Unscramble word solver to find your best possible play!



Www Orange K12 Nj Us Cms Lib Nj Centricity Domain 15 5energy Textbook V 1 1 1 Pdf




Do Newtonian Mechanics And Thermodynamics Have Different Definitions Of Internal Energy Physics Stack Exchange
Medical MGH abbreviation meaning defined here What does MGH stand for in Medical? Solved Examples Example 1 A 15 kg box falls at angle 25 ∘ from a height of 10 m Determine the work done by gravity Solution Given Mass m = 10 kg, angle = The work done by gravity formula is given by, W = mgh cos θ W = 15 × 98 × 10× =15 × 98 × 10× = 1332 J Therefore, the work done by gravity is 1332 J Example 2Example 5 My daughter Katrien, grabs my son's Niels leg and drags him 23 m across the floor If she exerted a force of 81 N to do this, determine how much work she did W = F d = 81 N (23 m) = 19 J When you look at the answer you just calculated, you'll also want to keep in mind the first definition of work



1
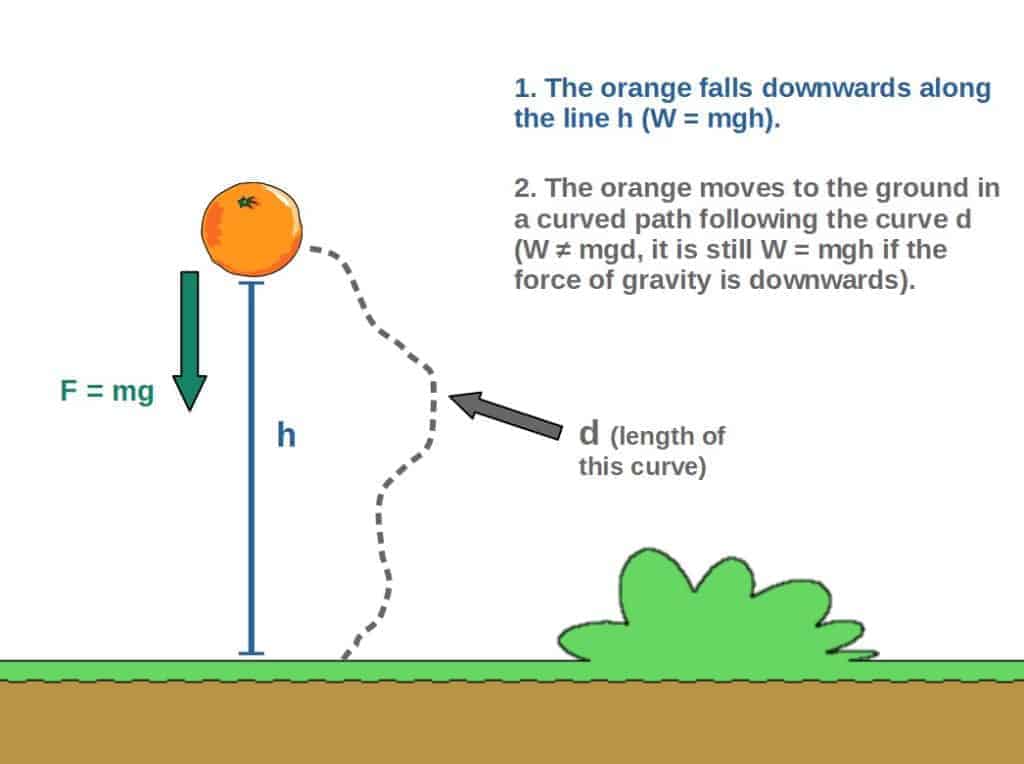



Does Gravity Do Work With Step By Step Examples Profound Physics
Related Words that start with mgh, Words that end in mgh Scrabble Words With Friends WordHub Crossword 12 letter words containingFor example, if a 0500kg mass hung from a cuckoo clock is raised 100 m, then its change in gravitational potential energy is mgh = (0500 kg)(980 m/s2)(100 m) = 490 kg⋅m2/s2 = 490 J m g h = (0500 kg) (980 m/s 2) (100 m) = 490 kg ⋅ m 2 /s 2 = 490 JDisclaimer Our interview questions and answers are created by experienced recruiters and interviewers These questions and answers do not represent any organization, school, or company on our site Interview questions and answer examples and any other content may be used else where on the site




Work Done By Gravity Path Independent Video Khan Academy



1
The height, h = 50 m; The Value of MGH Research and What it Will Take to Advance it Let's start with a little history In the middle of the th century, the National Institutes of Health ( NIH) was born, coincident with the dawn of the molecular approach to understanding medicine and human physiology The combination spawned a nationwide explosion of grantM m m = mass kg v v v = velocity m/s Energy has units of joules in the metric system 1 joule is the same as a 2 kg mass moving at 1 m/s Energy is a scalar It has no direction Not having to work with vectors can make solving 2D and 3D problems much easier




Htpibreview Ch6 P Mgh T Example Youtube




Electric Potential Gravitational Potential Energy A Gpe Mgh
W= mgh The displacement over which the work is done equals the height of the lift (d = h) Work Becomes Stored Energy This work which is done on the object as it is lifted does not end up as energy of motion, or kinetic energy, since, after the lift, the object is not moving;Mgh = ½ mv 2 In the above example mgh = 2,800 J ½ mv 2 = 2,800 Changing the subject v = \( \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 2,800}{\text{m}}}\) Since, m = 5 v = \( \sqrt{\frac{5,600}{5}}\) v = 335 mB Light without a source




Gravitational Potential Energy Definition Formula Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Mgh Institute Of Health Professions 2 8 Examples Of Typical Programs Of Study
• The gravitational Potential Energy is equal to the work done and this is equal to the weight times the height •W = Ep= mgh • ExampleHow much work is done lifting a 10 kg book to the height of 1m?The work done on the mass is then W = Fd = mgh W = Fd = mgh size 12{ ital "W = Fd = mgh"} {} We define this to be the gravitational potential energy (PE g) (PE g) put into (or gained by) the objectEarth system This energy is associated with the state of separation between two objects that attract each other by the gravitational forceIt is stationary It is higher up, though



New Page 1




Can Work Be Negative Easy Explanation Examples What S Insight
This is a separate property from that of inertia, so we give this property the name gravitational mass • is a measure of how much matter there is inThe force of gravity, g =98 m/s 2 PE = mgh PE = (22 kg) (98 m/s 2 ) (50 m) E = 1078 kg m 2 / s 2 = 1078 J 2) You move to aMGH INSTITUTE OF HEALTH PROFESSIONS Charlestown Navy Yard 36 1st Avenue Boston, MA (617) Directions • Campus Tour




Potential Energy Geeksforgeeks




Ppt Chapter 6 Work And Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Year 1 Clinical The first year of ID fellowship in the combined MGHBWH program offers an intensive experience in diverse inpatient and outpatient clinical care First year fellows rotate through inpatient rotations at both the MGH and BWH, including rotations in general ID, transplantation ID (both solid organ and bone marrow), and on teamsA comprehensive reference and clinical practice tool that searches Anesthesia textbooks, videos, calculators, guidelines and more in a single resource Also covers surgery, critical care, pain, ultrasound and more For mobile access, create a free MyAccess account on the desktop version, then login with these credentials on your mobile deviceThe default parameters are w 0 b 032 h 10 seedpt ta wta You can use one of the first five flags to change these default parameters Examples Example 1 mriwatershed atlas T1 brain where T1 is the T1 volume and brain is the output brain volume




Worksheet Weck 4 Potential Energy And Electric Chegg Com




Work
Example A 5 kg box falls at angle 450 from a height of 10√2 m Determine the work done by gravity Solution Given Mass m = 10 kg, angle = 450 The work done by gravity formula is given by, W = mgh cos θ W = 5 × 98 × 10√2 cos 450 = 490 JAll students are required to maintain a minimum cumulative grade point average of 30 each semester Failure to do so will result in a written academic warning issued by the appropriate Program Director Students who receive a written academic warning must regain a cumulative 30 GPA within the following semester or they will be subject toTo be specific,the work that you're talking about is the 'magnitude' of the work done by gravity on a body in raising it or dropping it through a height 'h' Now in general, the work done by any force 'f' in displacing a body through a certain dis



Chapter 6



Work Energy And Friction
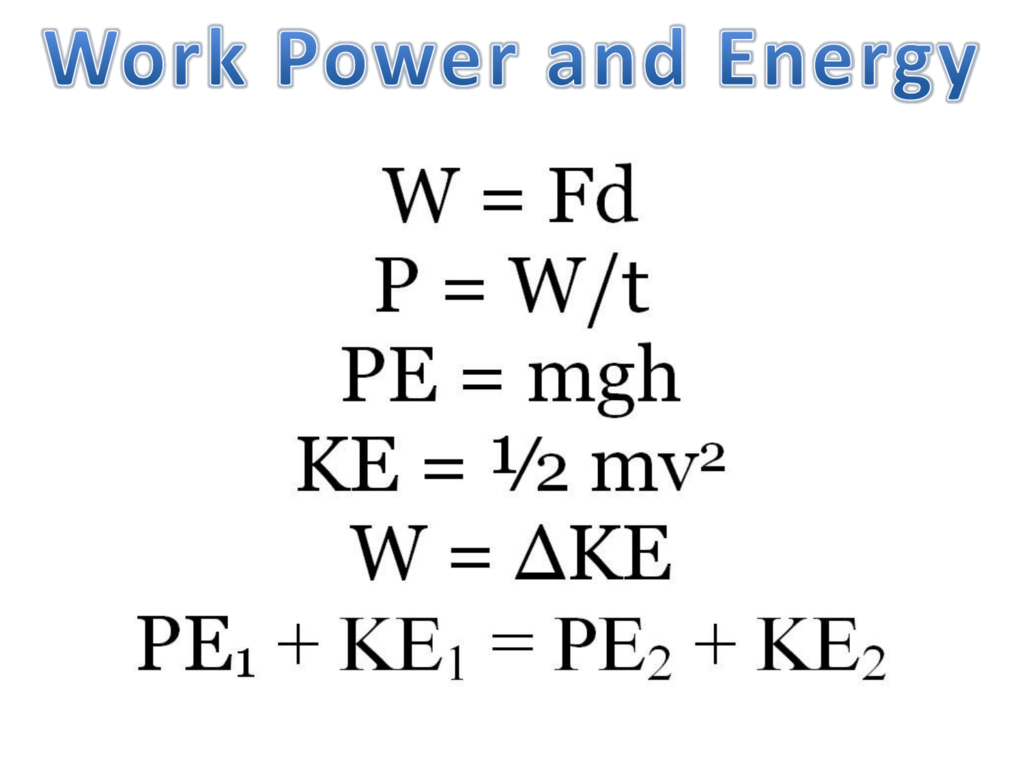
MGH INSTITUTE OF HEALTH PROFESSIONS Charlestown Navy Yard 36 1st Avenue Boston, MA (617) Directions • Campus Tour• Work = W = (10 kg) (98 m/s2) (1m) = 98 J • This is also the amount of Epthat the book has at a height of 1m Section 42The work done equals the force required to move it upward multiplied with the vertical distance it is moved (remember W = Fd) The upward force required while moving at a constant velocity is equal to the weight, mg, of an object, so the work done in lifting it through a height h is the product mgh
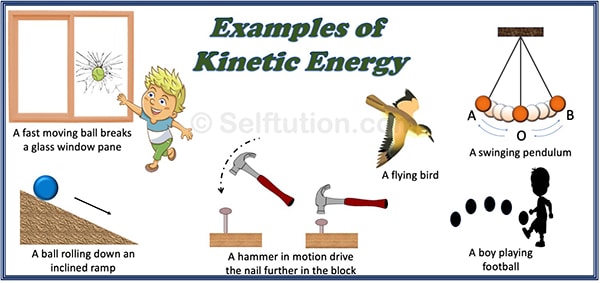



Difference Between Potential And Kinetic Energy Examples Selftution



Http Www Phy Ilstu Edu Bkc Phy102 Work Pdf
From the above equation W = mgh m = (sled) 80 (driver) 45 (equipment) *10 (dogs) m = 345 kg g = 981 m/s² (gravity constant) Work = W = F*s In case of gravitation, F = m*g, and s could be represented by h (height) The work done equals the change of potential energy So potential energy U = W = mgh #6 cragar 2,552 3 i thought work was the change in kinetic energy I Do you have an example of a truly random phenomenon? W = mgh It means the higher an object the higher will be its Gravitational PE Examples of gravitational potential energy in everyday life In many situations, it seems through energy has been stored in a system, to be recovered later For example, you must do work to lift a heavy stone over your head



Www Deanza Edu Faculty Lunaeduardo Documents Potentialenergyconservativef Pdf



Unit 4 Work And Energy Physics Project
At Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) provides parent guidance consultation to parents, and their partners, who are facing cancer or other lifethreatening medical illnesses Focusing on honest communication to support children's resilient coping, the PACT parent guidance modelGet the top MGH abbreviation related to MedicalThe Human Anatomy and Physiology II (HA&P2458 DL) course is the second of the two Human Anatomy and Physiology courses that will help provide the prerequisite foundation for graduate health professional school This course builds on information learned in Human Anatomy and Physiology I and includes details regarding the anatomy and physiology of the endocrine,




Energy Kaiserscience



2
Examples Example 1 pctsurfcon s bert Bugs None See Also wmanatsnr Links None Methods Description description description References References/Lastname### Reporting Bugs Report bugs to Author/s(12) $ \displaystyle W = mgh = 3000 \times \times $ = 701 megajoules Note This is a multipage article To navigate, use the dropdown lists Work done, W = mgh or W = 1960 × 5 = 9800 J Example 6 A boy pulls a toy cart with a force of 100 N by a string which makes an angle of 60º with the horizontal so as to move the toy cart by a distance horizontally Calculate the work done Solution Given F = 100 N, s = 3 m, θ= 60º Work done is given by W = Fs cos θ= 100 × 2 × cos 60º
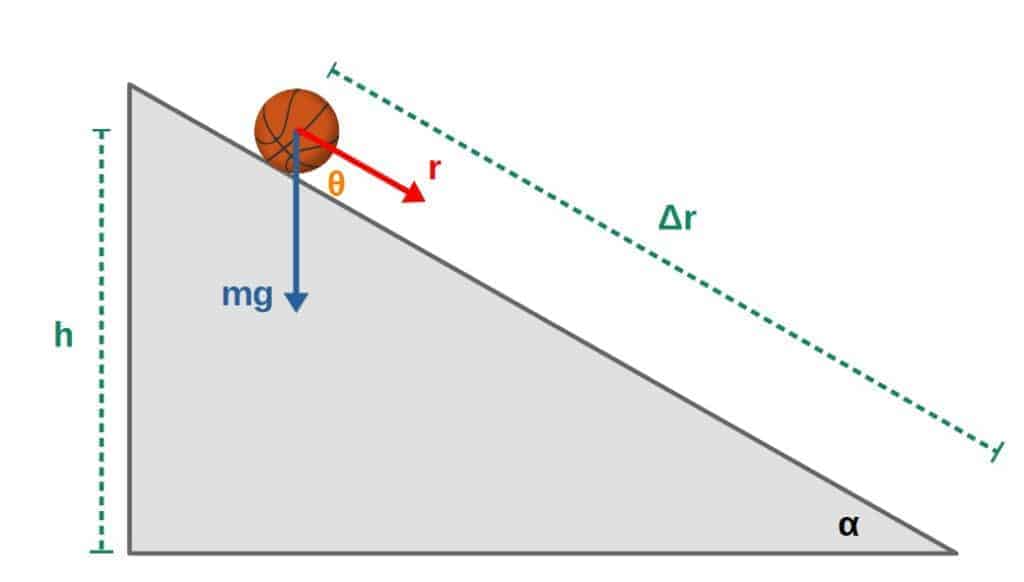



Does Gravity Do Work With Step By Step Examples Profound Physics
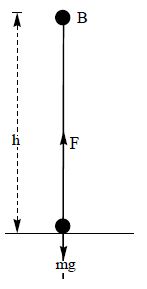



Work Energy And Power Practically Study Material
Gravity is an example h y m A B A mg d W = F cos φ d = mgh W = ( mg sin θ ) d = ( mg sin θ ) h sin θ = mgh W = mgh mg mg d θ B C • Nonconservative Force a force for which the work done depends on the path friction air resistance C dW = (Force)(Distance) = F D The footpound combines a unit of force a pound with a unit of distance a foot and is thereby a unit of work or energy 1 footpound is the amount of work that must be done to raise a 1 pound weight by 1 foot This also gives the change in potential energy of the 1 pound weightTitle MGHVisitorMap_ Created Date 1/4/21 600 PM



Www Physics Purdue Edu Webapps Index Php Course Document Index Phys214 1225 58 6860




Gravitational Potential Energy Mammoth Memory Physics




Work And Energy Potential Energy Pe G Mgh Kinetic Energy Ke Mv 2 Work W Fd Ppt Download
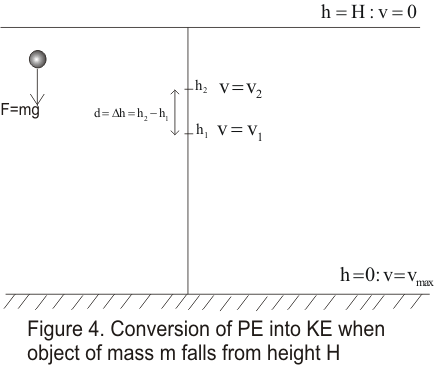



Potential Energy Gravitational Potential Energy




Potential Energy Geeksforgeeks



2
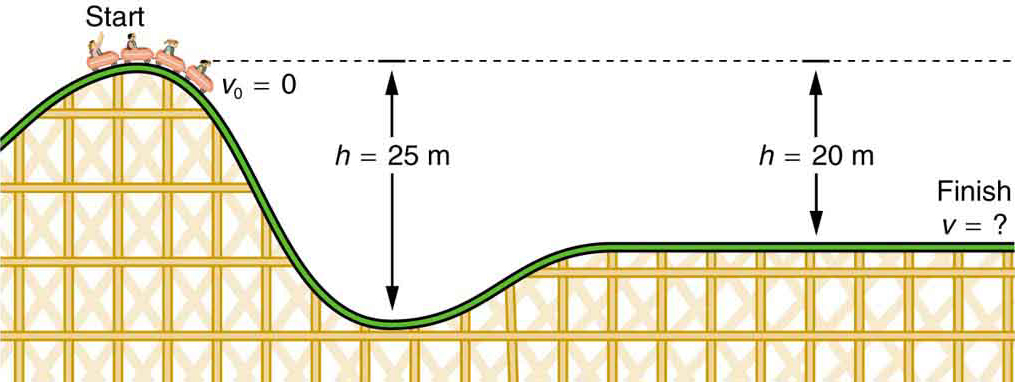



Gravitational Potential Energy Physics




Gravitational Potential Energy Ppt Video Online Download




100 Instructive Calculus Based Physics Examples The Laws Of Motion By Chris Mcmullen Paperback Barnes Noble
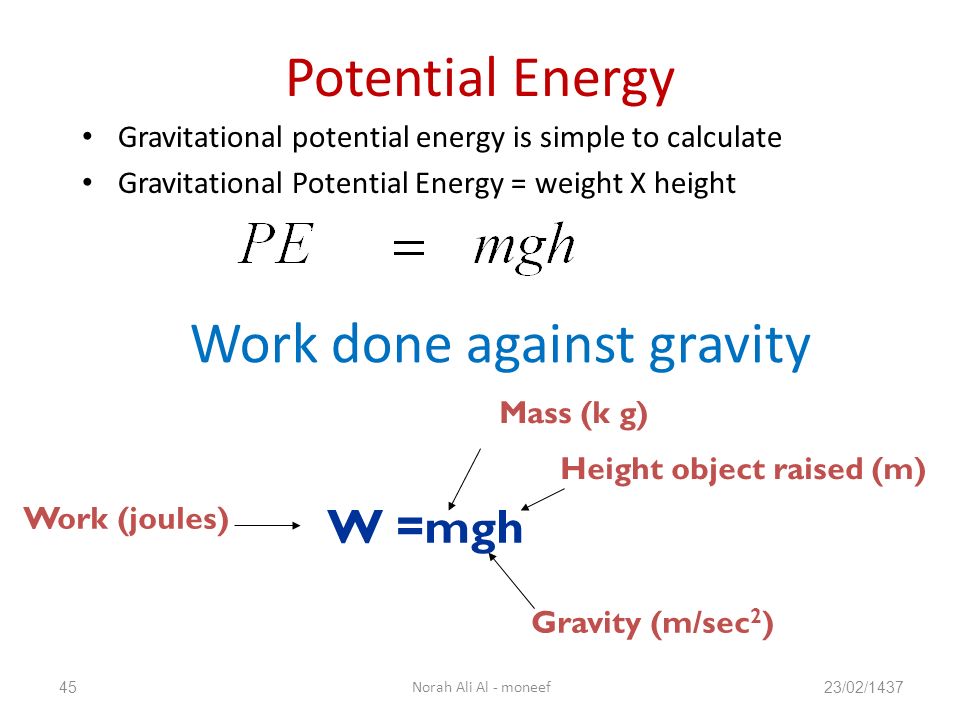



Chapter 6 Work Energy And Power Ppt Video Online Download



2




Gravitational Potential Energy Emedicalprep



Difference Between Potential And Kinetic Energy Examples Selftution



1




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics




Electric Potential Gravitational Potential Energy A Gpe Mgh




Let Us Consider An Equaiton 1 2 Mv 2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of The Body Upsilon Its Youtube




Work Energy And Power Physics Summary Hs Tutorial




Work As The Transfer Of Energy Video Khan Academy



2



Gravitational Potential Energy Zona Land Education



S3 Amazonaws Com Scschoolfiles 747 Ch 9 4 Gravitational Potential Energy Pdf




Potential Energy Formula And Sample Problem Pinoy Techno Guide
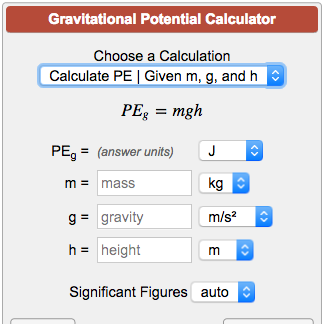



Gravitational Potential Energy Calculator



Http Www Ric Edu Faculty Psci103 Work Energy Work Lab Answers Pdf




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics
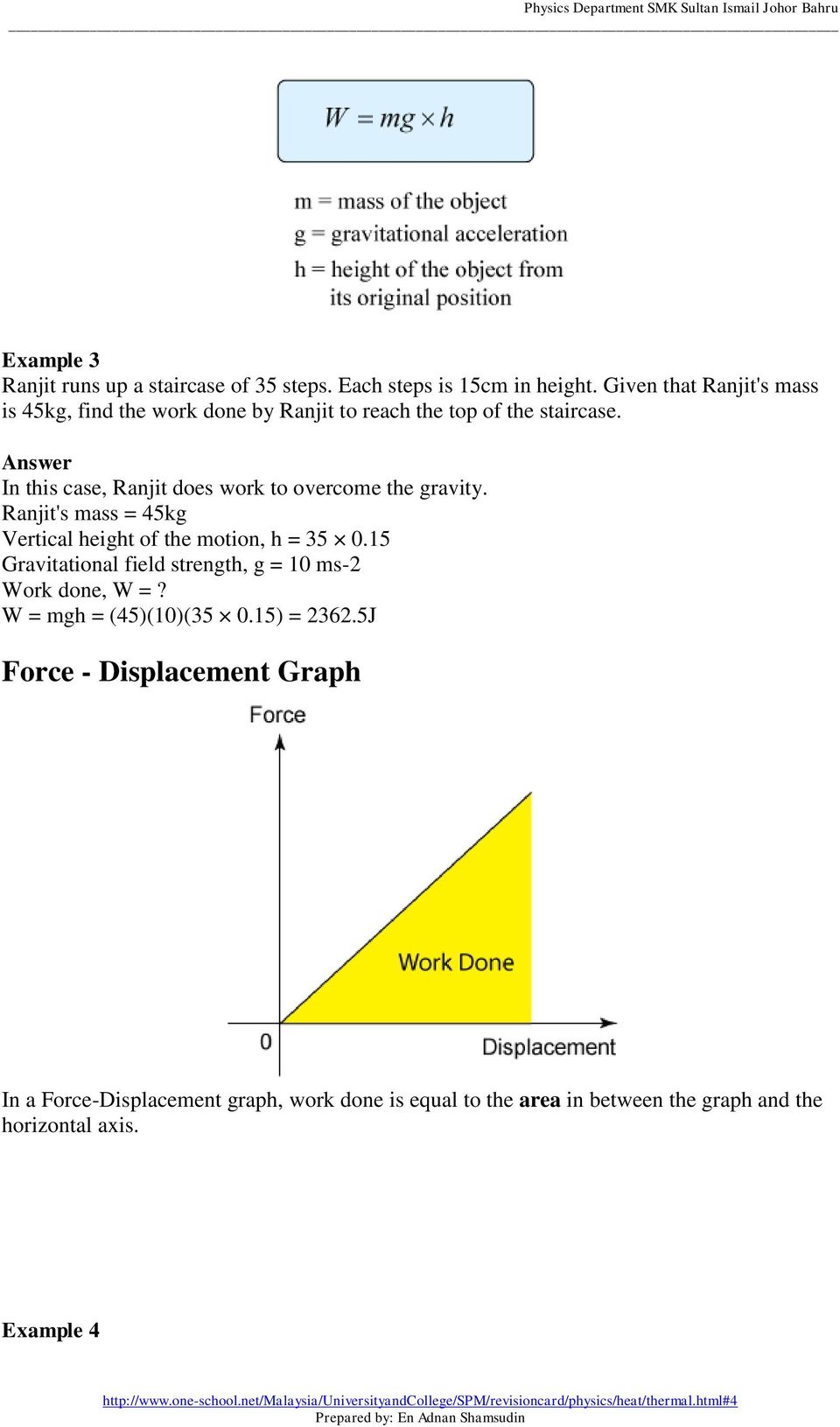



Weight The Weight Of An Object Is Defined As The Gravitational Force Acting On The Object Unit Newton N Pdf Free Download




Chapter 11 Energy And Its Conserv Chapter 11 Continued Energy Dart Kinetic Energy Chapter 11 Continued W Ke F Ke I Mv F 8 5 M S The Combined Mass Of The Bike Pdf Document




Lesson 2 Do Now 1 Energy Types




Prove Potential Energy P E Mgh With Figure Brainly In




Power Problems And Solutions Solved Problems In Basic Physics




Wmgh Derivation



7 Work And Kinetic Energy




11 17 Review Sheet Key For Work Power Energy




Htpib06c Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy Using Ep Mgh Youtube




Thermal Sys Physics Chpt10




Work Physics Definition Formula How To Calculate W Diagram Examples



Unit 4 Work And Energy Physics Project




Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf



Www Deanza Edu Faculty Lunaeduardo Documents Conservationofenergy Pdf



Gravitational Potential Energy Zona Land Education



1




Gravitational Potential Energy Emedicalprep




Kinetic Energy Formula Explanation And Example Proof M Is Mass V Is Velocity E 0 5mv 2gravitational Brainly In




Power Formula Derivation Of Power Formula Examples



Gravitational Potential Energy Video Lessons Examples Step By Step Solutions



Work Energy Power Powerpoint




Work And Energy Potential Energy Pe G Mgh Kinetic Energy Ke Mv 2 Work W Fd Ppt Download




Unit 1 Module 2 Work And Energy




Work And Energy Potential Energy Pe G Mgh Kinetic Energy Ke Mv 2 Work W Fd Ppt Download
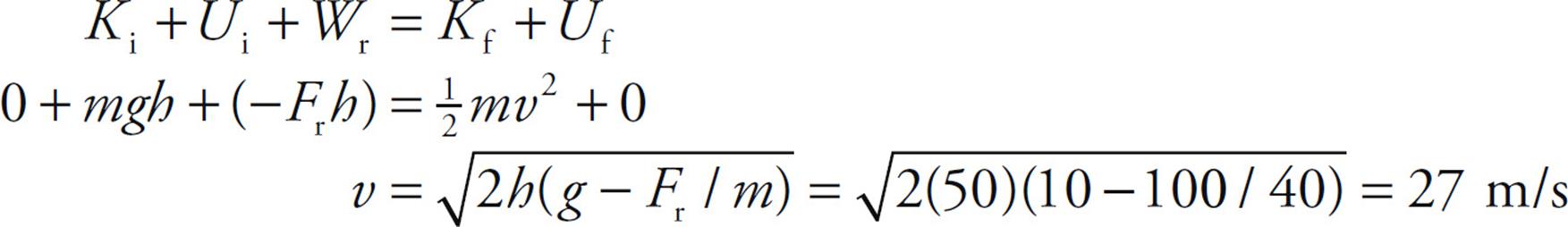



Work Energy And Power Content Review For The Ap Physics C Exam Ap Physics C Exam
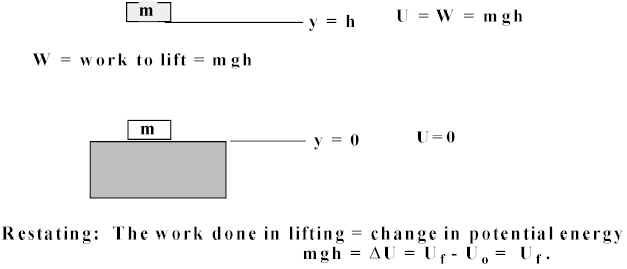



Simple Concepts Involving Work And Energy
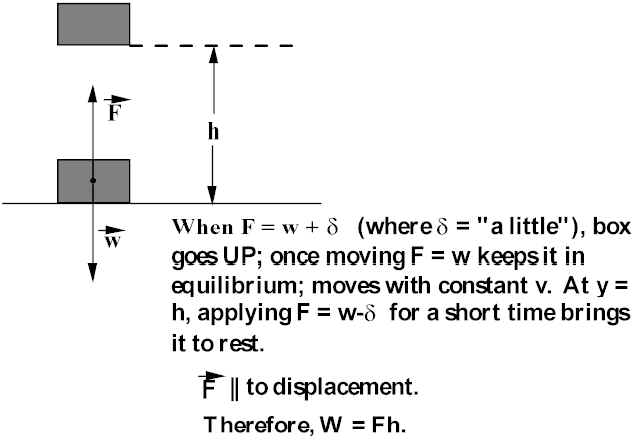



Simple Concepts Involving Work And Energy



S3 Amazonaws Com Scschoolfiles 747 Ch 9 4 Gravitational Potential Energy Pdf



Malaysia Pmr Spm Student S Learning Portal Provides Free Notes E Books References Formula List For Teachers Students For Tuition Or School Study Purposes



Mrmackenzie Co Uk Wp Content Uploads 07 02 Examples Of Potential Energy Problems Pdf




Subtle Concepts Of Work And Energy




What Is Work Done In Physics Defined Thecubics
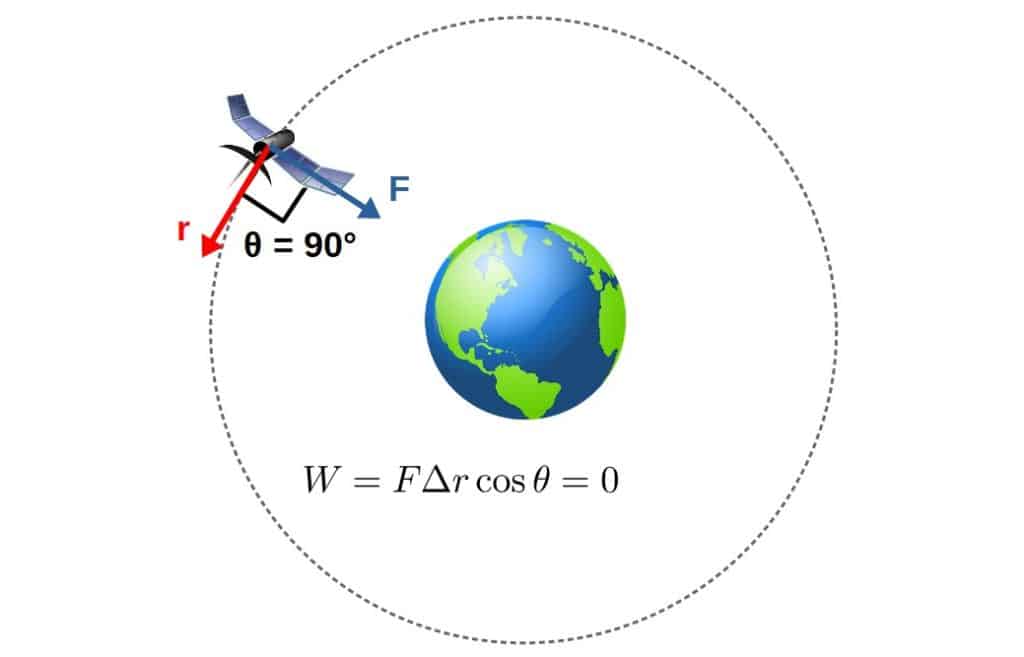



Does Gravity Do Work With Step By Step Examples Profound Physics




Tdbk66megdw9cm



Http Cosweb1 Fau Edu Jordanrg Phy48 Chapter 6 Notes 6 Pdf




Bestpixtajpl0sk 100以上 W Mgh Solve For H W Mgh Solve For H




Work



Work



Http Www Phy Ilstu Edu Bkc Phy102 Work Pdf



Http People Cas Uab Edu Mirov Lectures 10 11 chapter 8 fall 14 Pdf




What Is Potential Energy Potential Energy Examples




Kinetic And Potential Energy




Gravitational Potential Energy Pe Mgh Calculator




Understanding Work Energy Power Efficiency Energy Work Done
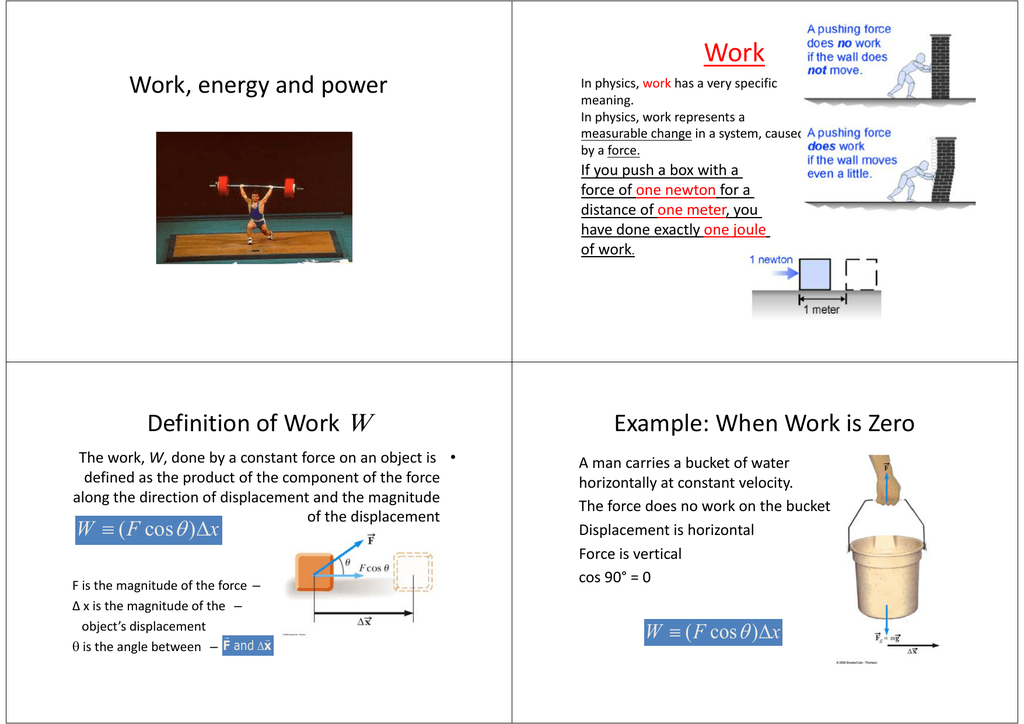



Work Energy And Power Definition Of Work W Example When Work
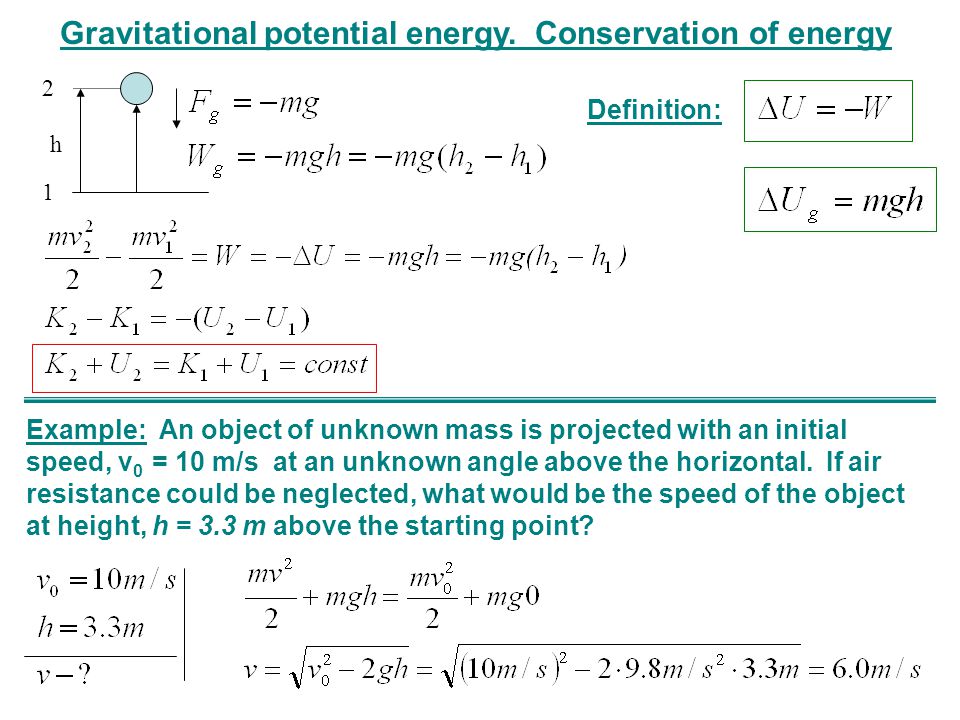



Gravitational Potential Energy Conservation Of Energy Ppt Video Online Download



Malaysia Pmr Spm Student S Learning Portal Provides Free Notes E Books References Formula List For Teachers Students For Tuition Or School Study Purposes




Worksheet Weck 4 Potential Energy And Electric Chegg Com



No comments:
Post a Comment